The LINX® difference
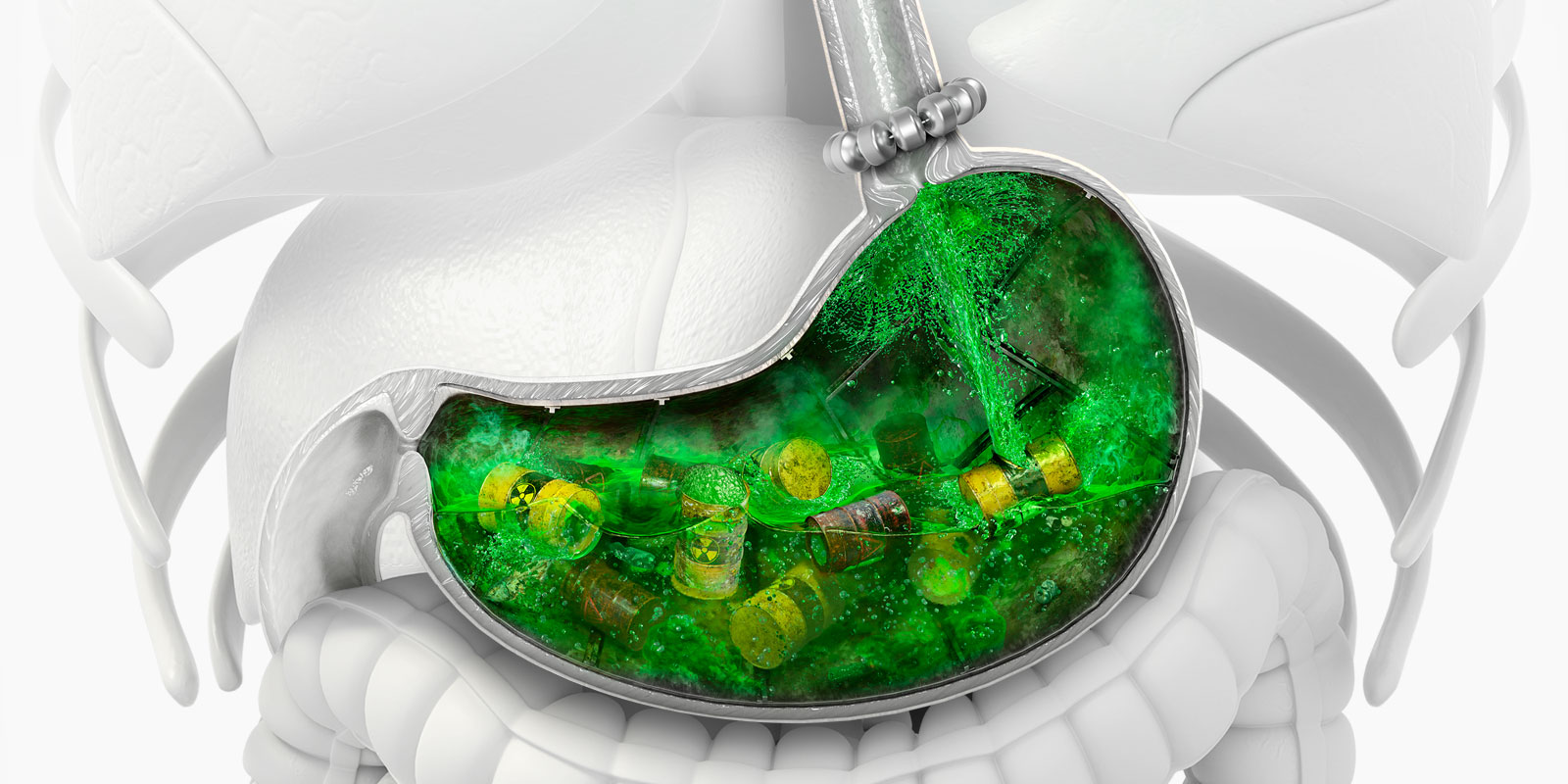
LINX is designed to work in harmony with the body to augment the weak sphincter without compromising the esophagus. the strength of the magnets is precisely calibrated to restore the Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) barrier function. the dynamic opening and closing of the beads preserves physiological function, allowing patients to belch and vomit. LINX is MRI compatible to 15T.
Simply designed to be simple.


Constructed of titanium and permanent magnets, LINX is placed around the LES during a minimally invasive procedure. the strength of the magnets helps keep the weak LES closed to prevent reflux. When patients swallow, LINX® opens temporarily to allow food and liquid to pass into the stomach.
Benefits of LINX®
Schedule a consultation
Contact us today and we’ll be happy to answer any questions you may have.

85% of patients achieved freedom from daily medication

Bothersome heartburn was eliminated in 88% of patients.

Bothersome regurgitation was eiminated in 99% of patients.

Decreased gas and bloating.

Patients reported a significant improvement in their Quality of Life.
Lower Esophageal Sphincter
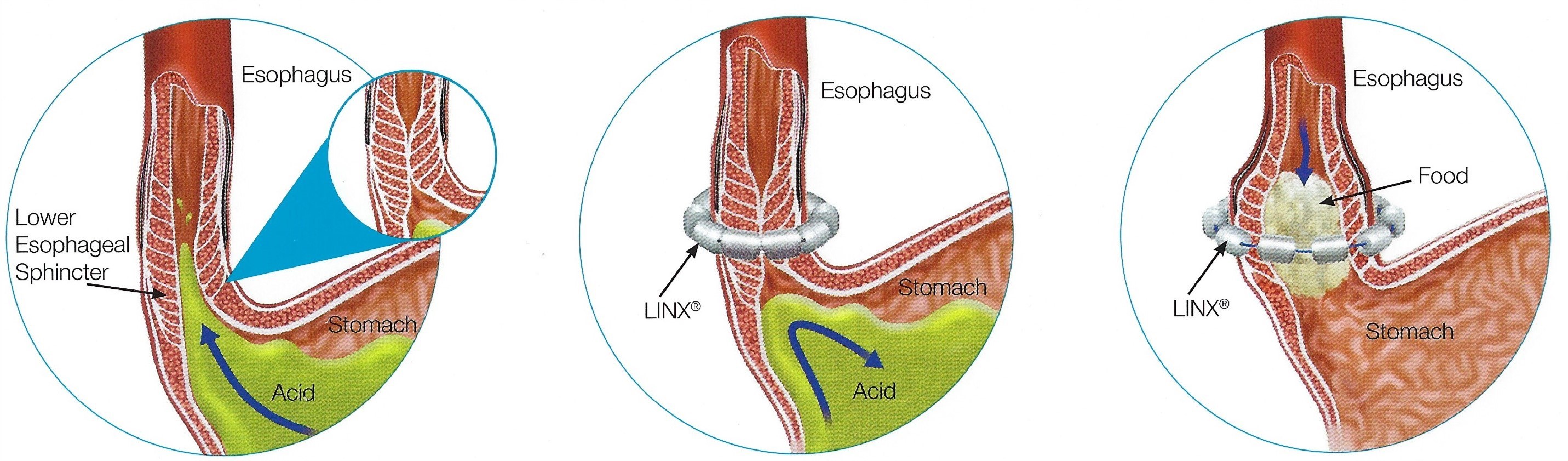
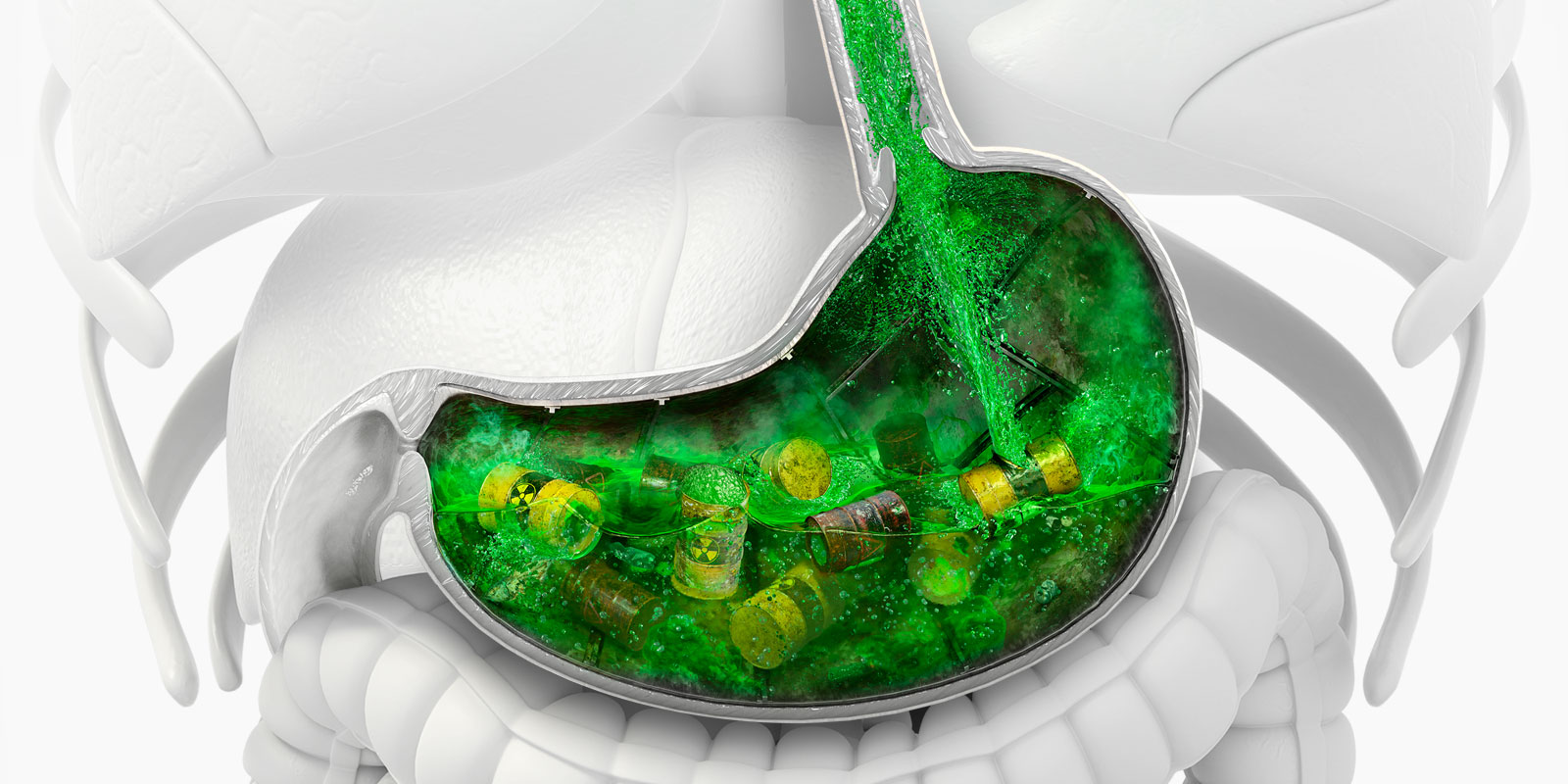
Reflux (also called Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, or GERD) is caused by a weak muscle in your esophagus called the Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) that allows acid and bile to flow back from the stomach into the esophagus, causing damage to the lining of the esophagus, throat, and lungs.
In addition to producing a wide range of symptoms, reflux disease can lead to serious complications including:
- Esophagitis (Inflammation that can damage the tissue of the esophagus)
- Stricture (Narrowing of the esophagus)
- Barrett’s esophagus (Pre-cancerous changes to the tissue lining the esophagus)
- Esophageal cancer
According to a study by the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, sufferers of Reflux disease who received a medical device like LINX saw a sharp reduction in Reflux symptoms within a year and remained sharply reduced for five years.
FAQ
Insurance companies and Medicare are approving patients for LINX® on a case-by-case basis. Once you have completed your pre-tests and are a candidate for LINX®, your surgeon will start the approval process.
LINX® is a small, flexible band of magnets that is surgically placed around the esophagus just above the stomach to help prevent reflux.
LINX® requires no alteration to the stomach, reduces gas and bloating, preserves the ability to belch and vomit, and patients generally go home within 24 hours and resume a normal diet
LINX® is placed around the esophagus just above the stomach using a minimally invasive surgical technique. the procedure lasts about an hour and many patients are able to go home the same day.
Yes. LINX can be removed using a minimally invasive procedure that generally lasts less than an hour and does not limit patients’ future treatment options.
Three diagnostic tests are used to determine if patients may candidates for LINX®: Endoscopy, pH, and Manometry
For patients with insurance, the out-of-pocket cost is based on your insurance plan, including deductibles and co-payments
Patients are encourages to return to a normal diet as soon as tolerated or as directed by their physician.
Patients are generally able to return to non-strenuous activity within a couple of days.
LINX® is designed to be a lifelong implant.
LINX® should not affect airport security. All patients are provided an implant card to let people know they have an implant.
Yes. LINX® patients may undergo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) up to either 0.7-Tesla (0.7T) or 1.5-Tesla (1.5T) depending on the LINX® model implanted. You should discuss the MRI scanning optios with your physician prior to deciding on treatment with LINX®. LINX® patients can also undergo: CT scan, x-ray, ultrasound and PET scan.
Belching, decreased appetite, device erosion, device migration (device does not appear to be at implant site), dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), flatulence, hiccups, inability to belch of vomit, infection, nausea, odynophagia (painful swallowing), pain, regurgitation, stomach bloating, weight loss, and worsening of preoperative symptoms.